Well you described something but nothing here is of any use to survivors.
Plantar Pressure and Contact Area Measurement of Foot Abnormalities in Stroke Rehabilitation
1
Sport Medicine and Physiotherapy Department, University of Craiova, 200585 Craiova, Romania
2
Faculty of Mechanics, University of Craiova, 200585 Craiova, Romania
3
Department of ECE, Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, Coimbatore 641114, India
*
Author to whom correspondence should be addressed.
†
All authors have an equal contribution.
Academic Editor: Giovanni Morone
Brain Sci. 2021, 11(9), 1213; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091213
Received: 18 July 2021 / Revised: 27 August 2021 / Accepted: 8 September 2021 / Published: 14 September 2021
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Balance, Gait and Falls in Peripheral and Central Neurological Disorders: From Pathophysiology to Rehabilitation)
Background:
Evaluation of plantar pressure in stroke patients is a
parameter that could be used for monitoring and comparing how the timing
of starting a rehabilitation program effects patient improvement.
Methods:
We performed the following clinical and functional evaluations:
initial moment (T1), intermediate (T2), and final evaluation at one
year (T3). At T1 we studied 100 stroke patients in two groups, A and B
(each 50 patients). The first group, A, started rehabilitation in the
first three months after having a stroke, and group B started after
three months from the time of stroke. Due to the impediments observed
during rehabilitation, we made biomechanic evaluation for two lots, I
and II (each 25 patients). Assessment of the patient was carried out by
clinical (neurologic examination), functional (using the Tinetti
Functional Gait Assessment Test for classifying the gait), and
biomechanical evaluation (maximal plantar pressure (Pmax), contact area
(CA), and pressure distribution (COP)).
Results:
The Tinetti scale for
gait had the following scores: for group A, from 1.34 at the initial
moment (T1) to 10.64 at final evaluation (T3), and for group B, 3.08 at
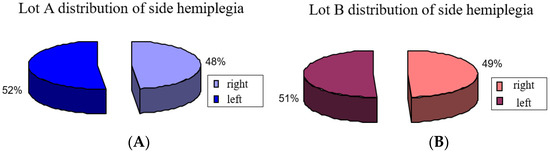
initial moment (T1) to 9 at final evaluation (T3). Distribution of COP
in the left hemiparesis was uneven at T1 but evolved after
rehabilitation. The right hemiparesis had uniform COP distribution even
at T1, explained by motor dominance on the right side. CA and Pmax for
lot I increased more than 100%, meaning that there is a possibility for
favorable improvement if the patients start the rehabilitation program
in the first three months after stroke. For lot II, increases of the
parameters were less than lot I.
Discussions:
The recovery potential is
higher for patients with right hemiparesis. Biomechanic evaluation
showed diversity regarding compensatory mechanisms for the paretic and
nonparetic lower limb.
Conclusions:
CA and Pmax are relevant assessments
for evaluating the effects on timing of starting a rehabilitation
program after a stroke.
View Full-Text
Keywords:
stroke; biomechanic evaluation; neurorehabilitation; plantar pressure; contact area; gait
▼
Show Figures
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited



No comments:
Post a Comment