http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fninf.2014.00089/full?
Tarek Sherif,
 Nicolas Kassis,
Nicolas Kassis,  Marc-Étienne Rousseau,
Marc-Étienne Rousseau,  Reza Adalat and
Reza Adalat and  Alan C. Evans*
Alan C. Evans*
- McGill Centre for Integrative Neuroscience, McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada
1. Introduction
BrainBrowser is an open source JavaScript library
exposing a set of web-based 3D visualization tools primarily targeting
neuroimaging. Using open web technologies, such as WebGL and HTML5, it
allows for real-time manipulation and analysis of 3D imaging data
through any modern web browser. BrainBrowser includes two major
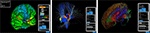
components. The BrainBrowser Surface Viewer (Figure 1)
is a WebGL-based 3D viewer capable of displaying 3D surfaces in real
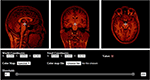
time and mapping various sorts of data to them. The BrainBrowser Volume
Viewer (Figure 2) is an HTML5 Canvas-based viewer allowing slice-by-slice traversal of 3D or 4D MINC volumetric data (Vincent et al., 2004).
FIGURE 1
FIGURE 2
In recent years, neuroimaging research has seen itself
inundated by large, distributed datasets that have necessitated a shift
in how scientists approach their research: guiding hypotheses are often
articulated after analyzing the mass of available data (Margulies et al., 2013), and data sharing has become a necessity for scientific discovery (Jomier et al., 2011).
Several large-scale, distributed, collaborative platforms have been
developed to facilitate this new approach, and they tend to integrate
poorly with traditional visualization tools requiring a local
installation and local data. These tools and their dependencies would
have to be installed locally, and data would generally have to be
exported from the platform in order to be visualized in the local
environment. Web-based visualization tools, on the other hand, present
significant benefits in the context of distributed research platforms:
No comments:
Post a Comment