Maybe with this your doctor and therapists could finally get exact diagnosis of your movement disabilities. And use that to correlate exact stroke rehab protocols that fix those disabilities. Pie in the sky I know but someone has to put goals out there. Your stroke medical professionals are doing nothing about goals to 100% recovery. You do want 100% recovery, don't you? And you've asked your doctor for protocols to get there? Haven't you? Did your doctor ask if you were crazy wanting 100% recovery? Or crazy just for asking?
Wearable tech aids stroke patients
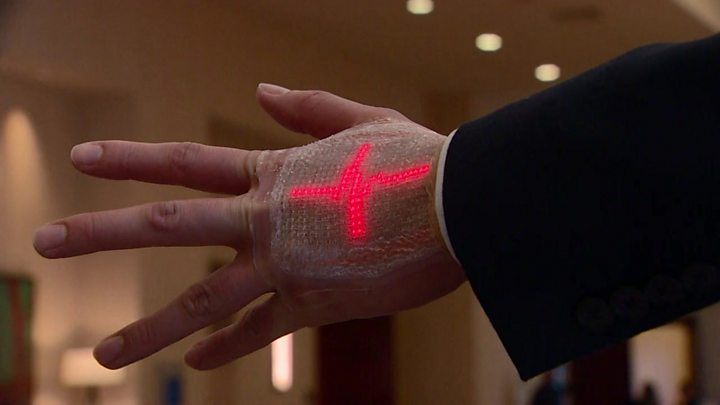

Scientists in the US are developing wearable sensors to speed up the recovery of stroke patients.
The sensors are able to send information to doctors continuously.
The team developing the system says it could allow therapists to more closely monitor the effectiveness of their care.
Details of the study were released at the recent annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Texas.
Lizzy McAninch had a stroke two years ago. She could not move or speak or swallow for several weeks.
Lizzy is testing out wearable sensors that might speed her recovery.
They look like small white sticking plasters, but they send information wirelessly to her medical team.
She is a doctor herself and can see how they could help her.
 Shirley Ryan AbilityLab
Shirley Ryan AbilityLab
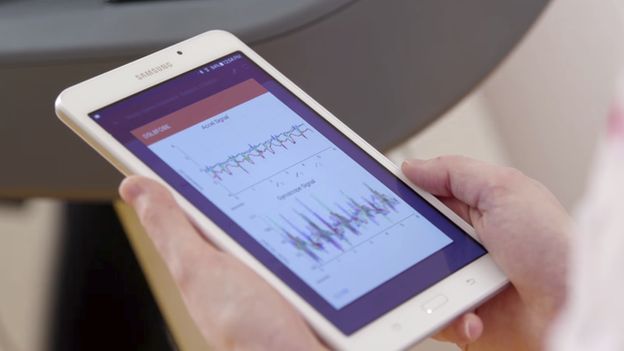
"This technology to put sensors on the body to assess which muscle groups work or not can really pinpoint the areas affected by the stroke and can target therapies to specifically improve those issues," she told BBC News.
The sensors continue to send back readings even after she has finished her exercises. This means that her therapist Kristen Hohl, from the Shirley Ryan AbilityLab in Chicago, can monitor her progress at home.
"As a therapist, I think about what my patients are doing at home. Are they able to carry through the recommendations I'm giving them as a therapist to do more? Do we see that they are walking more or do we see them engaging in conversations?
"Those are the types of things that I can get feedback from the sensors where currently I have to rely on what they tell me they have done."
 Shirley Ryan AbilityLab
Shirley Ryan AbilityLab
The challenge for the scientists was to pack a lot of electronics on to a small flexible material and still make it comfortable for the patient to wear for a long time.
"It is almost mechanically imperceptible to the patient who is wearing the device," according to John Rogers, of Northwestern University in Chicago, who developed the sensors.
"And you can embed all sorts of advanced sensor functionality, microprocessor computing capability, power supplies and WiFi into this very unusual platform, and that is the uniqueness of what we do."
By the end of this year, the research team will have more information than ever before on stroke recovery. The scientists believe that their study could transform the way patients are treated in the future.
No comments:
Post a Comment