But this is in mice, we don't have ANY STROKE LEADERSHIP WE CAN GO TO TO GET THIS RESEARCHED IN HUMANS. Stroke survivors will continue to be screwed until all stroke associations and hospitals are run by survivors. They have been incompetent for decades and don't deserve any more time. I had not heard of the 30 day problem, even more proof that the 'Use it or lose it' statement is wrong.
Novel complement inhibitor improves ischemic stroke recovery in mice, say researchers
Administering a novel complement protein blocker (B4Crry) alongside reperfusion therapy improved cognitive and motor
recovery in a model of ischemic stroke.
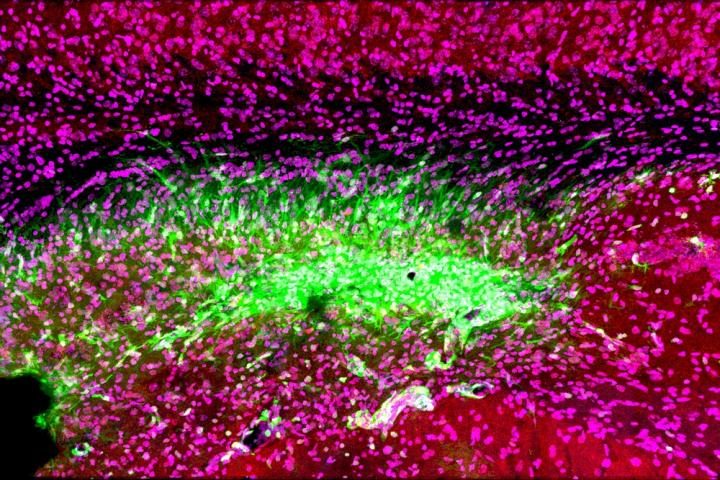 Even
after a blocked vessel has been opened, immune cells in the brain
(green) continue to attack synapses (red) and neurons (magenta) in the
memory center of the brain, the hippocampus, for at least 30 days after
stroke [credit: Medical University of South Carolina. Image courtesy of
Dr Stephen Tomlinson.].
Even
after a blocked vessel has been opened, immune cells in the brain
(green) continue to attack synapses (red) and neurons (magenta) in the
memory center of the brain, the hippocampus, for at least 30 days after
stroke [credit: Medical University of South Carolina. Image courtesy of
Dr Stephen Tomlinson.].Reperfusion therapy restores blood flow to an area of the brain after an ischemic stroke – a stroke caused by a blood clot blocking blood flow to an area of the brain. However, despite being the gold standard of treatment for ischemic strokes, only 10 percent of patients qualify due to its narrow treatment window (ideally given up to four hours after stroke, ineligible after eight hours).
Also, while blood flow is restored in 90 percent of patients, only 40 percent recover their motor and cognitive skills enough to cope with independent living within three months. Researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC), US, believe this is because while blood flow is restored, an ongoing inflammatory and phagocytic response to the damaged tissue results in further degeneration and damage.(Yep, call this the correct name: NEURONAL CASCADE OF DEATH)
This tagging of stressed neurons results in viable cells being destroyed, further exacerbating the damage to neuronal circuits and so researchers at MUSC sought to salvage them. The team developed a novel complement protein blocker, called B4Crry, which is designed to act only at the site of a stroke injury and blinds the complement proteins to the signals of stressed brain cells, preventing them being tagged.
When B4Crry was administered to a murine model of ischemic stroke alongside reperfusion therapy, the cognitive and motor abilities of mice improved. Evidence of co-ordinated movement recovery was visible even three days after the stroke with B4Crry, where there was no recovery with reperfusion therapy alone. In memory tasks, mice treated with B4Crry made three times fewer errors in a learning and memory task, while their reperfusion therapy only counterparts had the same recovery as mice that went completely untreated.
Complement inhibition and reperfusion safety
The team also demonstrated that after clot removal adding B4Crry to reperfusion therapy reduced the potential for haemorrhage, a complication associated with late administration of reperfusion therapy, even with treatment given up to six hours after the stroke. The team concluded that not only could complement inhibition make reperfusion therapy more effective and safer, but also extend the treatment window.The team are excited about the possibly using the complement protein blocker in clinic:
Lead author Dr Ali Alawieh, who completed his graduate studies at MUSC and is now a resident in neurosurgery at Emory University School of Medicine, revealed: “Our next step is to see how complement inhibitors work with comorbidities, such as old age, smoking and diabetes, in a preclinical study. Collectively, this information will help us design the best clinical trial when we move to humans.”Dr Stephen Tomlinson, interim chair of the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at MUSC and senior author of the article, said they are also testing whether the complement inhibitor may be beneficial in treating other brain injuries, such as traumatic brain injury.
“We have shown that we can administer complement inhibitors as far as two months after a traumatic brain injury and see improvements in cognitive recovery,” said Tomlinson. “This is something I’m actually quite excited about. It means that months after an initial event, complement inhibitors could still be beneficial to cognitive recovery after brain injuries, including strokes.”
The paper was published in the Journal of Neuroscience.
No comments:
Post a Comment