Don't do anything with this until research comes in 50 years from now.Unless you really really think your doctors and hospital are going to get research going prior to that.
Post-Ischemic Brain Neurodegeneration in the Form of Alzheimer’s Disease Proteinopathy: Possible Therapeutic Role of Curcumin
1
Laboratory of Ischemic and
Neurodegenerative Brain Research, Mossakowski Medical Research
Institute, Polish Academy of Sciences, 02-106 Warsaw, Poland
2
Department of Neonate and Infant Pathology, Medical University of Lublin, 20-093 Lublin, Poland
3
Department of Pathophysiology, Medical University of Lublin, 20-090 Lublin, Poland
*
Author to whom correspondence should be addressed.
Academic Editor: Maria Antonietta Panaro
Nutrients 2022, 14(2), 248; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020248
Received: 18 December 2021
/
Revised: 1 January 2022
/
Accepted: 3 January 2022
/
Published: 7 January 2022
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioactive Natural Compounds for Therapeutic and Nutraceutical Applications in Neurodegeneration)
For thousands of years, mankind has been using plant extracts or plants
themselves as medicinal herbs. Currently, there is a great deal of
public interest in naturally occurring medicinal substances that are
virtually non-toxic, readily available, and have an impact on well-being
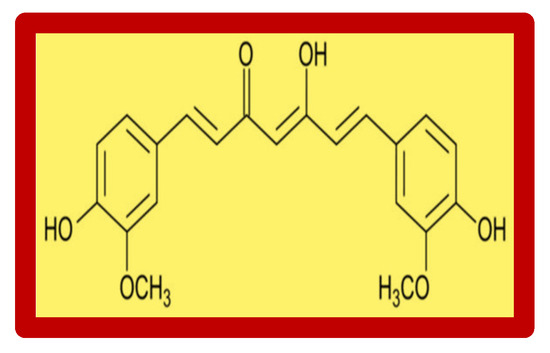
and health. It has been noted that dietary curcumin is one of the
regulators that may positively influence changes in the brain after
ischemia. Curcumin is a natural polyphenolic compound with pleiotropic
biological properties. The observed death of pyramidal neurons in the
CA1 region of the hippocampus and its atrophy are considered to be
typical changes for post-ischemic brain neurodegeneration and for
Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, it has been shown that one of the
potential mechanisms of severe neuronal death is the accumulation of
neurotoxic amyloid and dysfunctional tau protein after cerebral
ischemia. Post-ischemic studies of human and animal brains have shown
the presence of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. The
significant therapeutic feature of curcumin is that it can affect the
aging-related cellular proteins, i.e., amyloid and tau protein,
preventing their aggregation and insolubility after ischemia. Curcumin
also decreases the neurotoxicity of amyloid and tau protein by affecting
their structure. Studies in animal models of cerebral ischemia have
shown that curcumin reduces infarct volume, brain edema, blood-brain
barrier permeability, apoptosis, neuroinflammation, glutamate
neurotoxicity, inhibits autophagy and oxidative stress, and improves
neurological and behavioral deficits. The available data suggest(This is why your doctor and hospital need to initiate research) that
curcumin may be a new therapeutic substance in both regenerative
medicine and the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders such as
post-ischemic neurodegeneration.
View Full-Text
Keywords:
brain ischemia; neurodegeneration; curcumin; neuroprotection; amyloid; tau protein; dementia
▼
Show Figures
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited


No comments:
Post a Comment