Will your competent? doctor guarantee that the protocol they are writing up on this will 100% prevent Alzheimers? Why not? Can they at least get human testing going? Or are they that fucking incompetent in not knowing of that need?
All this earlier research which I bet your doctor/hospital knows nothing!
Do you prefer your doctor and hospital incompetence NOT KNOWING? OR NOT DOING?
Arginine slows amyloid buildup and improves brain outcomes in Alzheimer’s disease models
New preclinical evidence shows that oral arginine reduces toxic amyloid structures and eases behavioral impairments in Alzheimer’s models, highlighting a potential therapeutic path that now requires careful human dose and safety evaluation.
Study: Oral administration of arginine suppresses Aβ pathology in animal models of Alzheimer's disease. Image Credit: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
A recent study published in the journal Neurochemistry International showed that arginine suppresses amyloid beta (Aβ) pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease (AD) models. AD is the most common dementia, affecting more than 50 million individuals worldwide. The aggregation of Aβ peptides into fibrils and oligomers is likely the upstream event in the pathogenesis of AD. While various therapies have been developed targeting Aβ, they have limited efficacy, adverse effects, and high costs. As such, safe and cost-effective orally administered therapeutic approaches to inhibit Aβ aggregation are needed.
Rationale for Testing Arginine as an Anti-Aggregation Agent
Previously, the authors showed that arginine suppresses the aggregation of polyglutamine (PolyQ) proteins, exerting therapeutic effects in preclinical models of PolyQ diseases. Moreover, oral arginine administration was found to improve patients with spinocerebellar ataxia type 6, a PolyQ disease. Given that arginine is a chaperone that inhibits protein misfolding and aggregation, the authors hypothesized that it might suppress the aggregation of Aβ.
In Vitro Assays Demonstrate Strong Inhibition of Aβ Aggregation
In the present study, researchers investigated whether arginine suppresses the aggregation of Aβ in preclinical models of AD. First, they examined the suppression of Aβ aggregation in vitro and incubated Aβ42 peptides in the presence of varying concentrations of arginine. The aggregation of Aβ42 peptides was determined by Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence intensity.
The team observed that co-incubation of Aβ42 and arginine substantially reduced ThT fluorescence intensity in a dose-dependent manner, decreasing Aβ42 aggregation by 80% at 1 mM arginine. Electron microscopy showed that fibrils were shortened, and biochemical analyses indicated reduced insoluble Aβ42 fractions with unchanged soluble Aβ42 levels, consistent with reduced fibrillar aggregation.
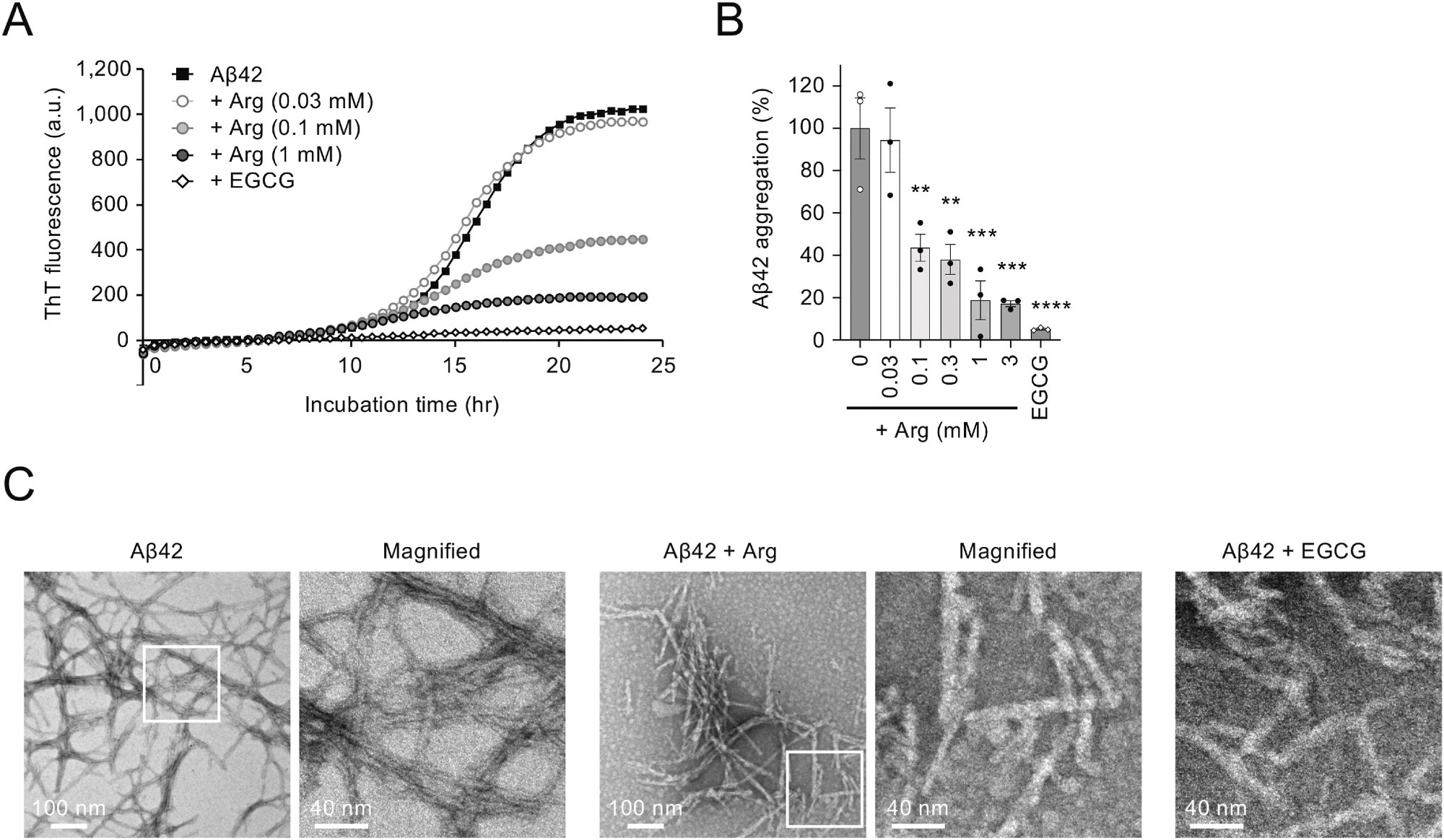
Arginine suppresses Aβ42 aggregation in vitro. (A) Effect of arginine on Aβ42 aggregation in vitro. The incubation of Aβ42 peptide (5 μM) at 37 °C resulted in an increase in Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence after a short lag phase, which eventually reached a plateau. (B) Bar graph showing the ratio of Aβ42 aggregation in the presence of arginine at 24 h. (C) EM images of Aβ42 amyloid fibrils. Scale bars, 100 nm (left images) and 40 nm (right images). The panel on the right is a magnified image of the boxed region in the left panel. Statistical analysis in (B) was performed to assess differences from the control group (Aβ42 without arginine) by one-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
Arginine Reduces Amyloid Deposition in Drosophila AD Models
Next, the researchers examined in vivo suppression of Aβ aggregation in a Drosophila AD model carrying the Aβ42 transgene with the E22G Arctic mutation (Aβ42arc). Aβ42arc expression in the compound eyes led to abnormal deposition in larval eye discs and shrinkage of adult eyes due to Aβ toxicity. However, oral arginine administration substantially decreased Aβ42 deposition and suppressed eye shrinkage in a dose-dependent manner.
Mouse Studies Show Reduced Amyloid Deposition and Plaque Burden
The team further evaluated arginine in App knock-in mice carrying Arctic, Beyreuther, or Iberian, and Swedish mutations (AppNL-G-F mice), which develop age-dependent Aβ deposition and behavioral abnormalities. The mice received 6% arginine orally from 5 weeks of age. Body weight did not differ between treated AppNL-G-F, untreated AppNL-G-F, or wildtype mice.
No comments:
Post a Comment