Your doctor should know all this with your risk of Parkinson's.With no objective test for Parkinson's, it's difficult. My Dad took forever to get diagnosed, the only symptom he had was the 6-8 inch shuffling gait at least until he became non-verbal.
Parkinson’s Disease May Have Link to Stroke March 2017
The latest here:
Aging or Parkinson’s? Here Are 13 Essential Ways You Can Tell Photo by sruilk from Shutterstock
Photo by sruilk from Shutterstock
Aging is a natural, beautiful process we should all be proud of. Every wrinkle, every word, and each gesture marks all the things we’ve been through – things that made us who we are now.
Even when we get clumsy or we feel like we’re moving slower, it’s all part of this magical journey called life.
Or is it?
According to Parkinson’s Foundation, more than 60,000 Americans in our country are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease (PD) every year. A total of 10 million people around the world are living with this illness and many are still undiagnosed. Why?
Because Parkinson’s disease occurs in people older than 50, many of its symptoms are resembling the normal signs of aging.
However, there are a few early signs everyone should know in order to
detect the illness on time and get proper treatment. Today, we’ll
reveal 13 crucial symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and how they can
manifest. Image By Nata Bene From Shutterstock
Image By Nata Bene From Shutterstock
Loss of smell
This symptom now seems more frightening than ever since it’s also a common sign of COVID-19.
Tremors
This is one of the key signs of Parkinson’s disease although, as we’ve mentioned earlier, it can also be a normal sign of aging. How can you tell the two apart?
Tremors caused by early Parkinson’s include sudden twitching or shaking of the chin, hands or legs. Another particularity is that these tremors stop if the person starts moving the affected part of the body.
Since Parkinson’s is a progressive disorder, the tremors are initially so subtle only the affected person may notice them. However, they can become more frequent and intense over time.
Interestingly enough, tremors start manifesting only on one side of the body and extend gradually to the other side as well. Image By Andrey_Popov From Shutterstock
Image By Andrey_Popov From Shutterstock
Balance problems
Parkinson’s disease can affect many of your neuronal capacities,
especially basal ganglia. These tiny nerve cells are located deep inside
your brain and they’re essential for flexibility and balance. Photo by fizkes from Shutterstock
Photo by fizkes from Shutterstock
Difficulty walking
If a person starts walking strangely, you think you’d notice immediately, right?
When it comes to early Parkinson’s disease, even this symptom might be difficult to detect. We already know that this illness can affect your balance, but it can also have a negative impact on member coordination.
As a result, people with early Parkinson’s may start dragging their feet just a little as they walk, or they may walk slower than usual.
As the disease progresses, walking habits also become stranger: the affected person may experience an irregular pace, such as suddenly walking faster without actually wanting to.
Sleep problems
If this were the only symptom of Parkinson’s, I think the majority of us would suspect we have it, right?
Sleep problems can be caused by countless problems from physical and mental disorders to stress and unhealthy lifestyle choices. However, it can also be one of the earliest signs of Parkinson’s disease when it manifests as:
- Sudden fatigue
- Night terrors
- Uncontrollable movements during sleep
- Insomnia
- Sleep apnea
If you notice any of the above, the first thing you should do is
check your daily schedule and physical condition to eliminate any
alternative reasons. Image By Lena Nester From Shutterstock
Image By Lena Nester From Shutterstock
Facial masking
Did you know that we need at least 12 different facial muscles just for a shy smile? Our face is a wonder mechanism when it comes to the expressions we make to describe how we feel.
Unfortunately, though, Parkinson’s disease can also affect nerve cells in this area, which causes a symptom medically called facial masking.
In simple terms, a person with early Parkinson’s may no longer be able to make the facial expressions they desire. As the disease progresses, they gradually lose their ability to make any face expressions, which can make them seem emotionless, as if they’re wearing a mask.
A particularity of this symptom is that it might also cause a person to blink slower than usual.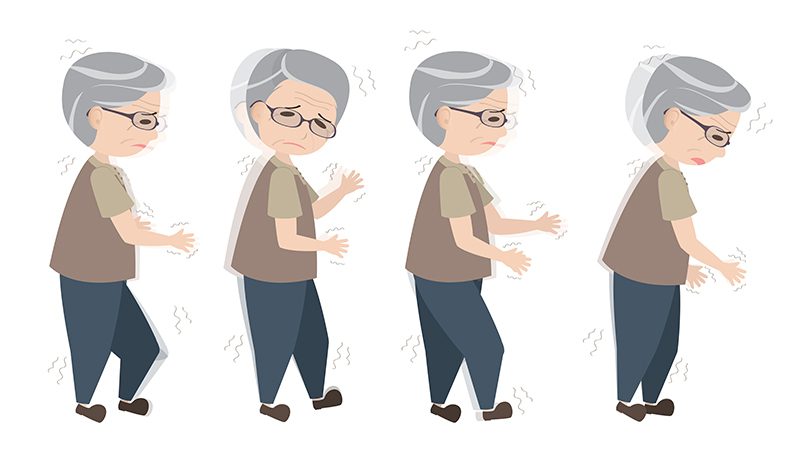 Image By bunnyphoto From Shutterstock
Image By bunnyphoto From Shutterstock
 Image By Rawpixel.com From Shutterstock
Image By Rawpixel.com From Shutterstock


No comments:
Post a Comment