1 Introduction
Owing to the high frequency, prevalence, disability
rate, and mortality rate of stroke, it has received widespread attention
from the global research community (GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators, 2021).
There is a large amount of scholarly literature on stroke, and numerous
studies have been published in leading medical journals. Many
researchers have conducted comprehensive meta-analyses to examine the
various factors related to stroke. However, systematic bibliometric
examinations providing a comprehensive view of publications, countries,
research institutions, journals, authors, and keywords in published
formats are lacking. This bibliometric study aims to fill this gap by
providing a detailed and insightful overview of the existing knowledge
in stroke research. Bibliometrics is an analytical discipline that uses
quantitative and statistical methods to study the production and
dissemination of scholarly literature (Hicks et al., 2015).
It involves careful collection, organization, and analysis of
bibliographic data such as citation counts, co-authorship networks, and
publication venues (Mukherjee et al., 2022).
The advantages of bibliometrics include their ability to quantify and
identify the impact of research, provide evidence-based evaluations of
scientific output, and track the progress and influence of research over
time. It also helps to identify emerging trends, developing fields,
collaborative efforts, and guide strategic planning and resource
allocation within research institutions (Jiang et al., 2023).
With the expanding volume of scientific literature and growing
importance of research impact, the role of bibliometrics in evaluating
and interpreting research has become increasingly important.
This study used a comprehensive bibliometric analysis to
assess the trajectory, breakthroughs, and key issues within the existing
stroke research. By summarizing and analyzing current findings and
trends, this study fills critical gaps in the existing literature,
providing researchers, clinicians, epidemiologists, and policymakers
with a refined and comprehensive perspective on the current state of
stroke research.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data retrieval strategies
We used the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC), the
most authoritative and comprehensive global science database, to search
for stroke-related literature. The search spanned articles uploaded to
the database on March 31, 2024. The search terms were as follows:
((((((TS = (stroke)) OR TS = (cerebral infarction)) OR TS = (ischemic
stroke)) OR TS = (intracerebral hemorrhage)) OR TS = (hemorrhagic
stroke)) OR TS = (subarachnoid hemorrhage)). Because of the absence of
animal testing or experimental protocols in our study, ethical clearance
was not required. Our selection criteria were confined to Highly Cited
Papers with document types of “article” or “review” in the English
language, targeting a specific subject matter and research objective,
and ensuring uniformity in language for subsequent analysis. All other
literature types and non-English articles were excluded from the review.
We conducted searches and examined all articles retrieved in various
formats on the same day in plain text form to create master files for
use with different bibliometric tools (Yeung, 2019).
Thereafter, we extracted essential information such as author names,
source of study, title, keywords, and cited references from the exported
articles to mitigate potential errors during retrieval at different
instances.
2.2 Bibliometric analysis
In this study, we employed R version 4.3.3 (Ihaka and Gentleman, 1996), VOSviewer (Van Eck and Waltman, 2010), and CiteSpace (Chen, 2006)
to conduct bibliometric analysis. We utilized the Bibliometrix R
package version 4.3.3 to calculate the frequency of international
collaboration among countries (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017).
VOSviewer was used to determine the numbers of publications, citations,
and keywords. The built-in clustering algorithm of the software enabled
the construction and visualization of co-occurrence networks of key
terms from scientific literature (Jiang et al., 2022).
Our main focus was on co-authorship and co-occurrence analysis, which
helped us to understand the collaboration between countries,
institutions, and authors.
We used CiteSpace to identify highly cited references and
keywords that had witnessed substantial citation growth over a specific
period. Using online bibliometrics, we visualized international
collaborations between countries. We analyzed the annual scientific
output and average citations per year using Microsoft Excel.
3 Results
3.1 Overview of publication status
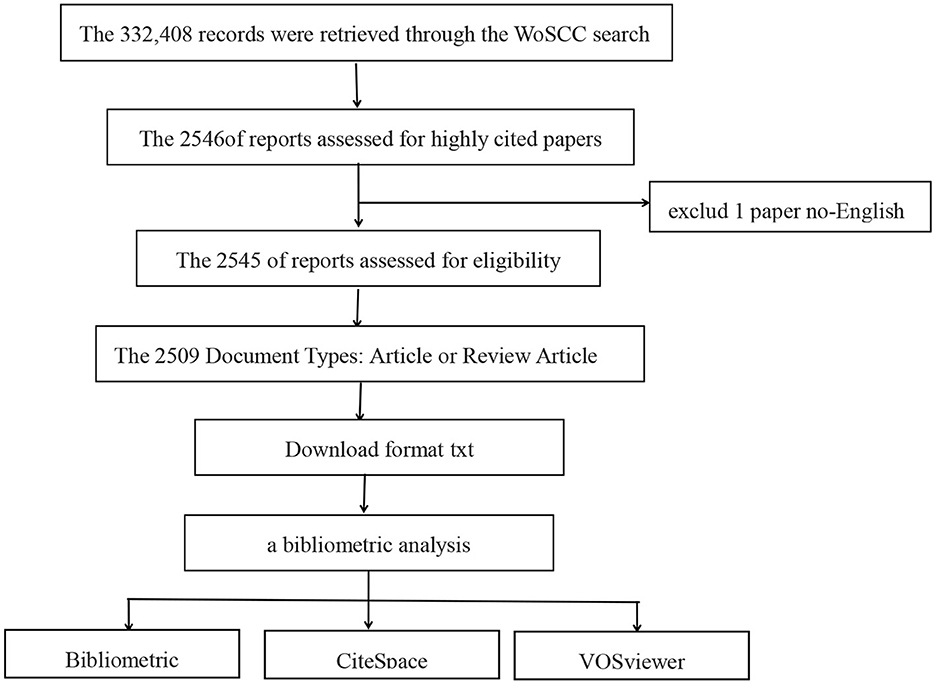
From the extensive collection of 332,408 research
studies, a selected group of 2,509 publications that had been
extensively referenced was identified for closer analysis. This
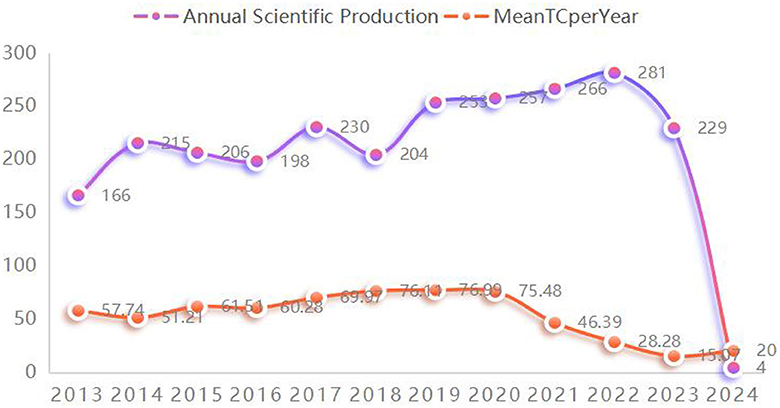
collection includes 1,749 articles and 760 reviews, as depicted in Figure 1. Figure 2
illustrates that the most recent of these highly cited papers on stroke
were released in 2024, with the earliest being from 2013. A review of
the most highly cited periodicals revealed that the annual volume of
scientific contributions will reach its zenith in 2022. In addition,
2020 saw the highest annual average number of citations per paper.
3.2 Analysis of national publication counts
To explore the distribution of research output across
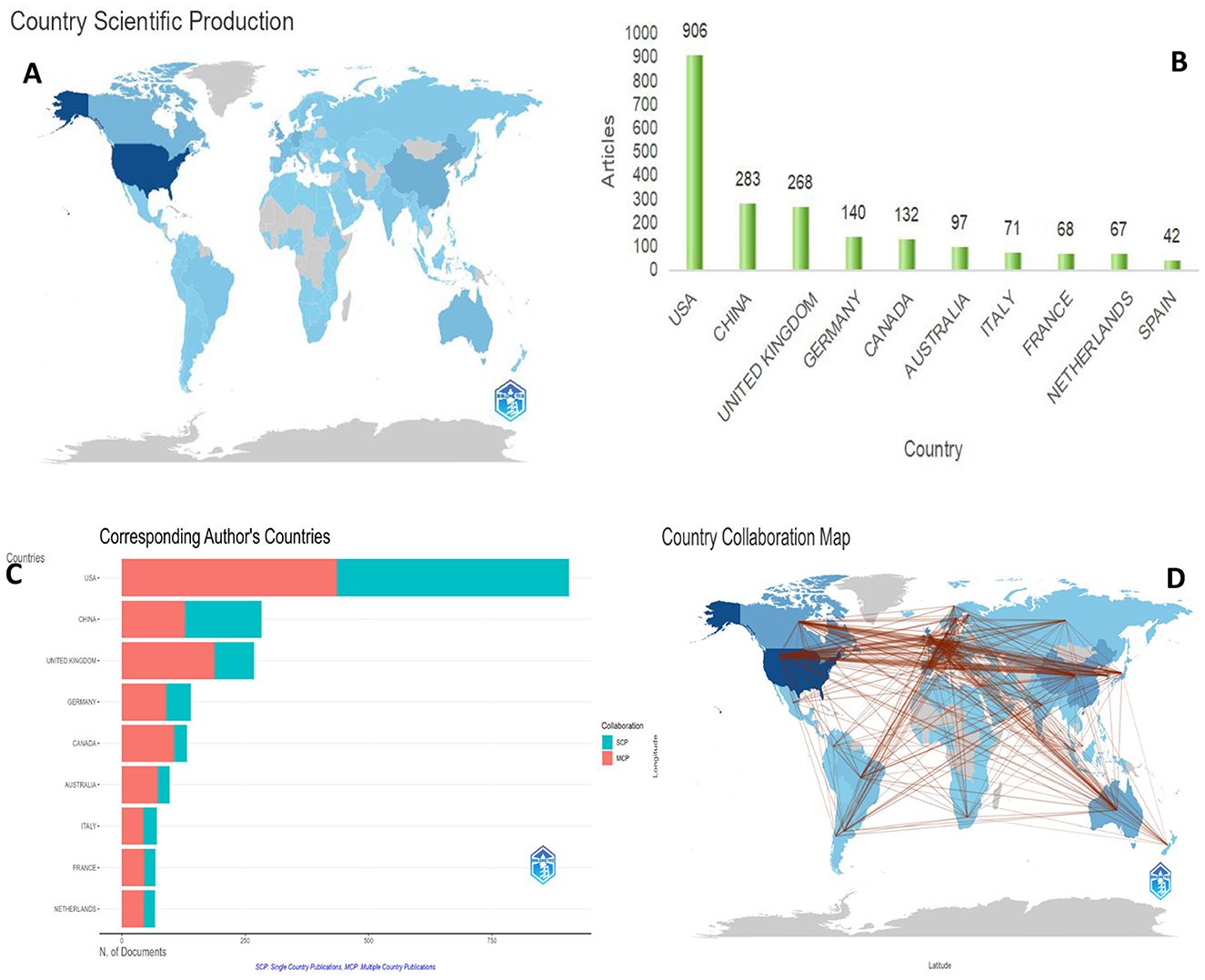
countries and regions, a comprehensive analysis of national publication
tallies was conducted (Figures 3A, B).
The dataset reviewed included research contributions from 113 countries
or regions and more than 5,186 distinct institutions. As depicted in Figure 3,
the United States emerged as the leading contributor, with 906
published works, followed by China (283), the United Kingdom (268),
Germany (140), and Canada (132). All other countries or regions included
in the analysis had a total publication count of < 100.
In addition to the overall output analysis, we mapped international collaborations in the field of stroke research, as shown in Figure 3D.
The findings revealed that the United States is at the forefront of
stroke research collaborations. There is a high degree of global
cooperation, particularly among the developed nations in Europe and
North America (Figure 3C).
The top 10 countries in terms of collaboration, the top 10 countries
had a median country-to-country partnership (MCP) ratio exceeding 45%
when collaborating with international authors. The United States
collaborated the most in the United Kingdom (420 times), Canada (365
times), and Germany (323 times). In the United Kingdom, the most
frequent collaborative partners were Germany (242 times) and Canada (241
times).
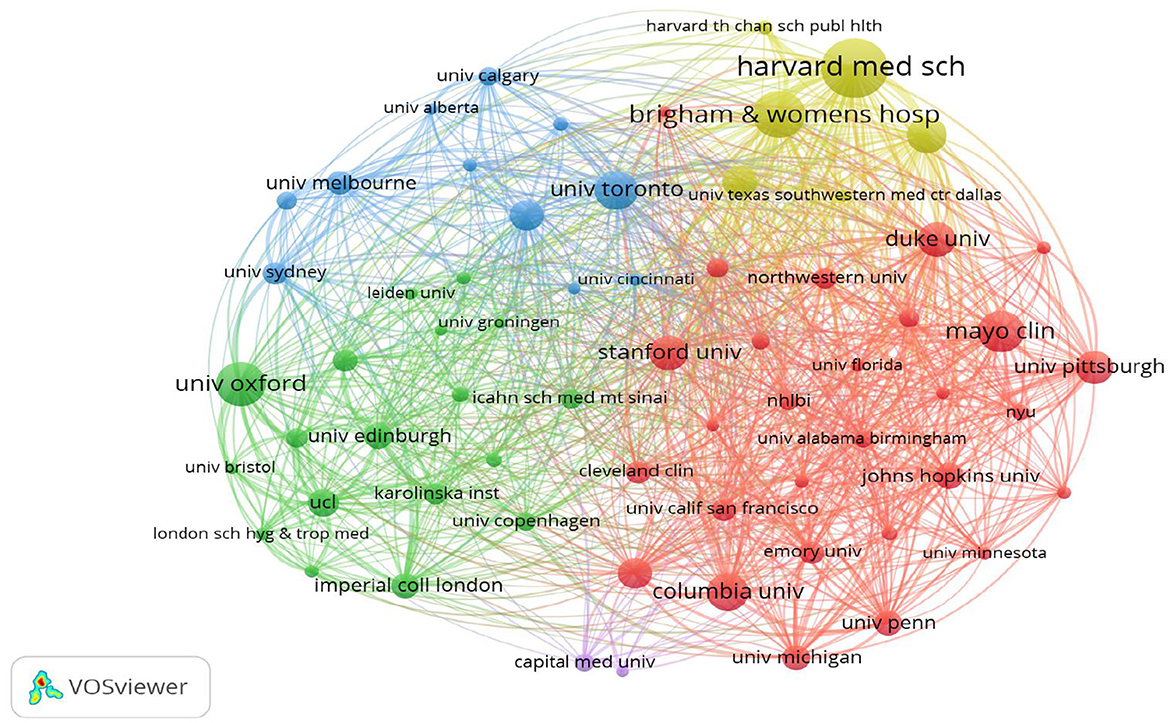
3.3 Analysis of institution publications
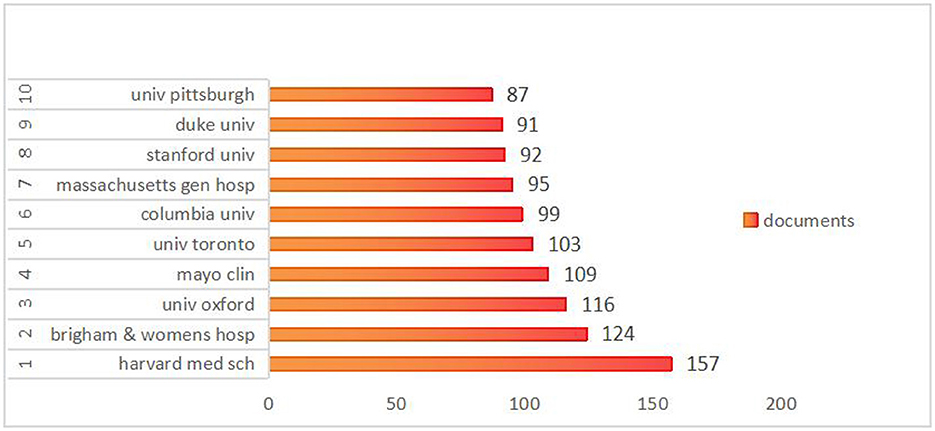
An analysis was conducted to examine the contributions of
various institutions to the domain of stroke research, which revealed
the publication output of nearly 5,186 institutions globally. As
depicted in Figure 4,
the five leading institutions published more than 100 papers, with
Harvard Medical School emerging as the leader with 157 publications.
Brigham and Women's Hospital closely followed the 124 publications.
Additionally, to delve deeper into collaborative efforts between
institutions, a co-authorship analysis was conducted across all
published papers. As shown in Figure 5,
68 institutions had published at least 25 papers. These 85 institutions
were clustered into four groups, with the red cluster being the most
prominent, comprising 36 members, primarily from the USA. The green
cluster was the second-largest cluster, consisting of 31 institutions.
The third cluster is the blue cluster with nine institutions, and the
smallest is the yellow cluster, which consists of eight institutions.
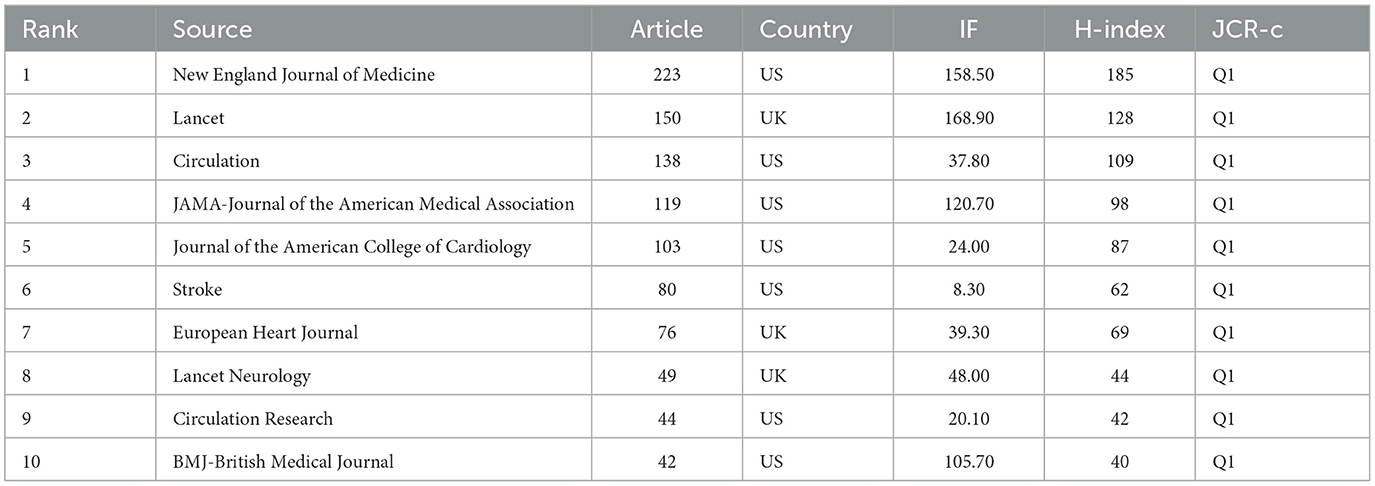
3.4 Analysis of publication quantity and journal impact
This study included 2,509 articles published in 590 journals. Table 1
lists the top 10 journals ranked by publication quantity and latest
2022 impact factors (IF). The top 10 journals were all top journals,
with an average impact factor of 73.13, and four journals had an
influence factor of more than 100. All top 10 journals were in the first
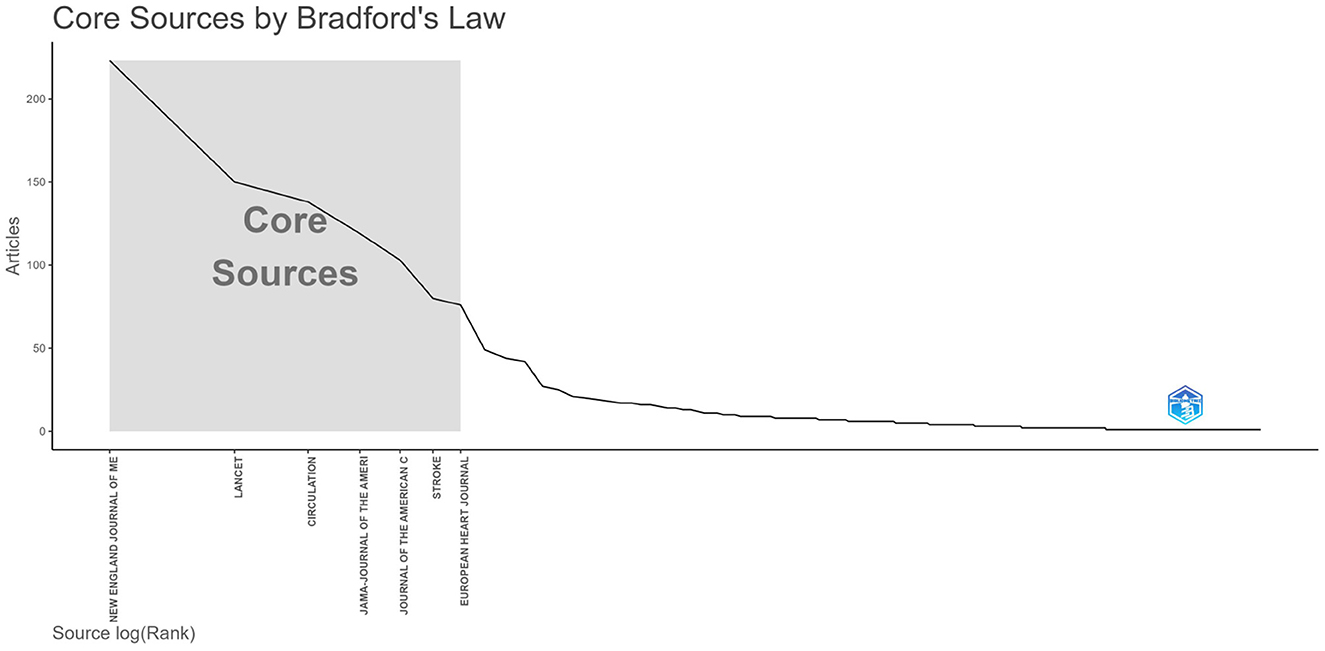
quartile (Q1) of the Journal Citation Reports (JCR). As shown in Figure 6,
we can see from the graph of Bradford's dispersion law that the core
journals in the research field include the top seven journals in terms
of their publications.
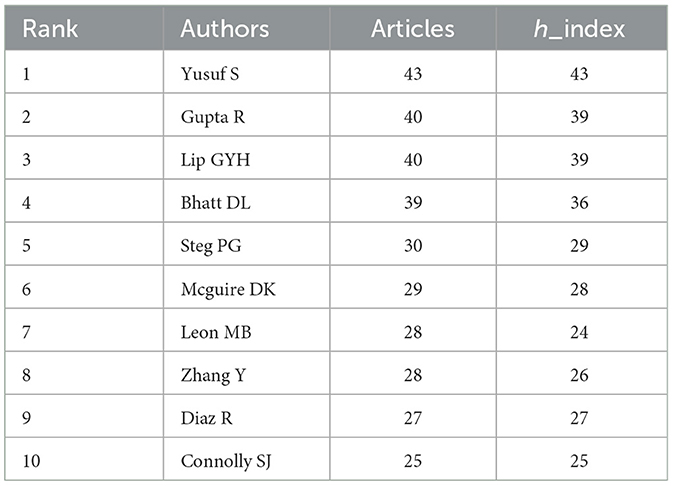
3.5 Author impact analysis
A comprehensive analysis of 15,324 contributors to
seminal stroke studies revealed that YUSUF S led the pack with 43
published studies and an H-index of 43. Second, GUPTA R and LIP GYH also
deserve mention, producing 40 articles each, with an H-index of 39 (Table 2).
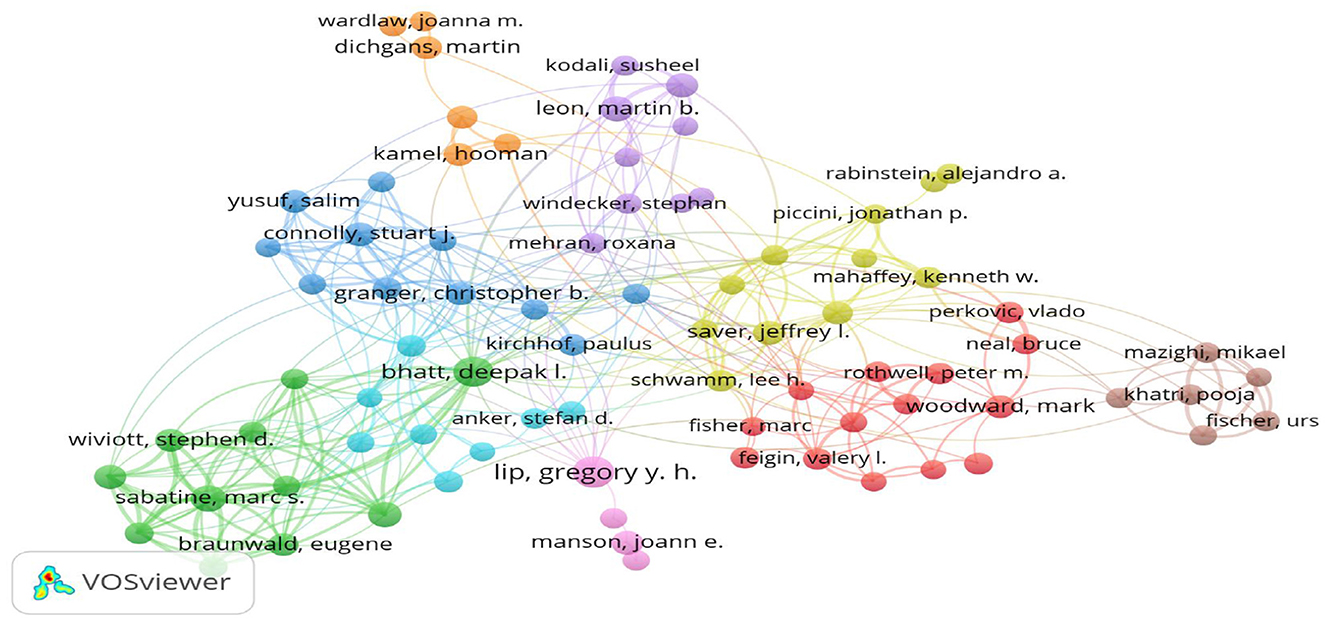
The collaborative networks among these researchers are depicted in Figure 7,
where the size of the nodes corresponds to the number of articles
authored, and the color coding denotes the clusters. Eighty authors,
each having published eight or more articles, were identified and
organized into nine clusters. These clusters exhibit mutually
cooperative patterns. The largest cluster comprised 14 research groups,
whereas the smallest contained only four research groups.
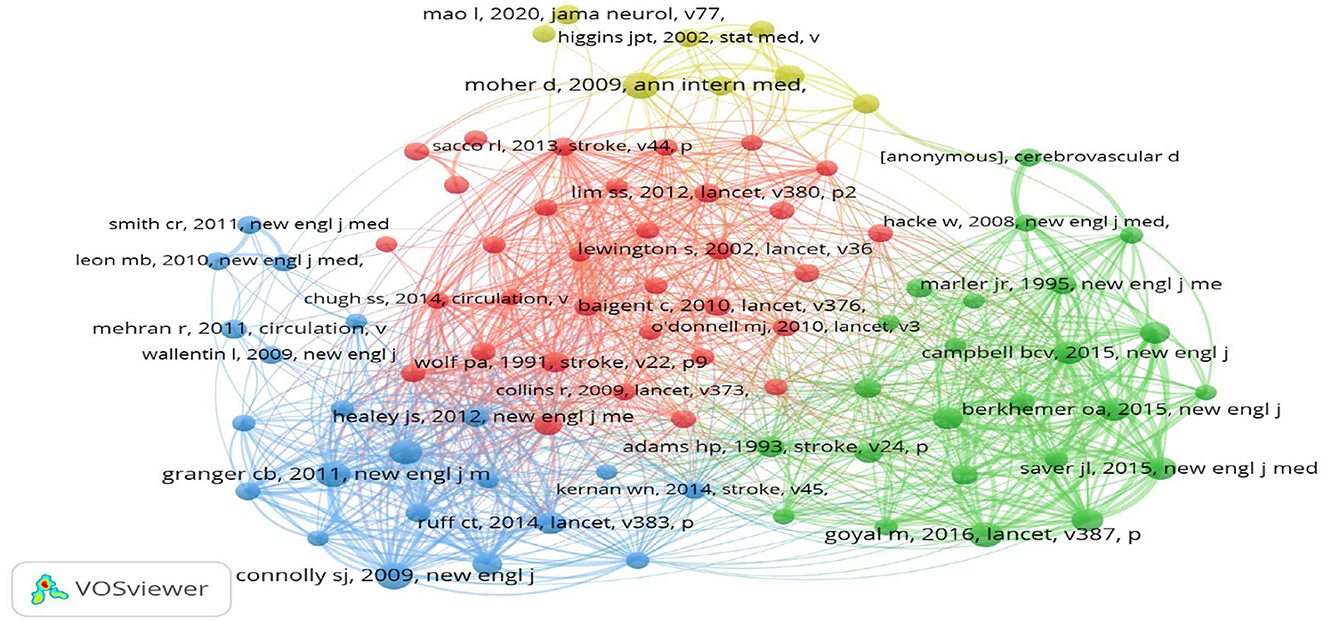
3.6 Co-cited references
Over the past 10 years, 172,373 references have been
cited in highly cited papers on stroke. To further explore the research
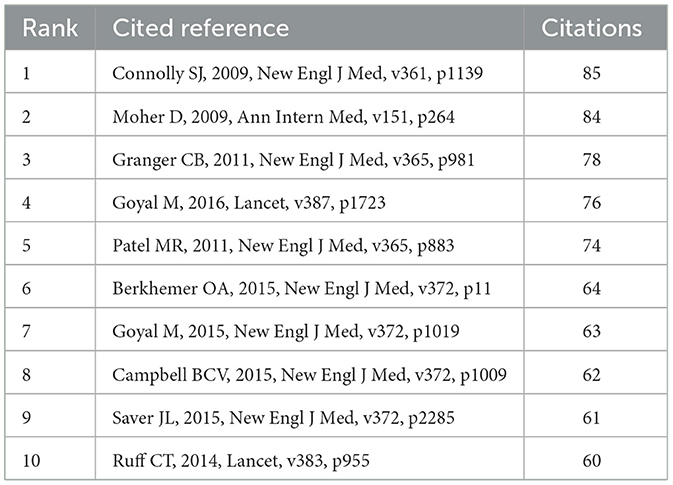
dynamics and trends in this field, we identified 10 articles with the
highest citation frequency (Table 3). In addition, 86 cited references were selected, and a co-citation network graph was generated with a threshold ≥30 (Figure 8). As shown in Figure 8,
a positive co-citation relationship is observed among articles
published in different years in the journals. There was one reference
published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2009 that has
received the most citations: “Dabigatran vs. warfarin in patients with
atrial fibrillation.” The results of this study demonstrate that
anticoagulation with 110 mg dabigatran and warfarin is equivalent in
patients with atrial fibrillation, with no significant difference in the
risk of preventing stroke and systemic embolism. However, in patients
receiving dabigatran, the risk of major bleeding was significantly lower
than that in those receiving warfarin. When the dabigatran dose was
increased to 150 mg, the risk of stroke and systemic embolism was
significantly lower in the treatment group than that in the warfarin
group, while the proportion of major bleeding remained stable (Connolly et al., 2009).
This finding provides an important reference for anticoagulation
therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation, showing the potential
advantages of dabigatran. The lowest-cited reference was published in
Lancet in 2014 (citation number: 63). The average citation value for the
first 10 cited references was 70.7.
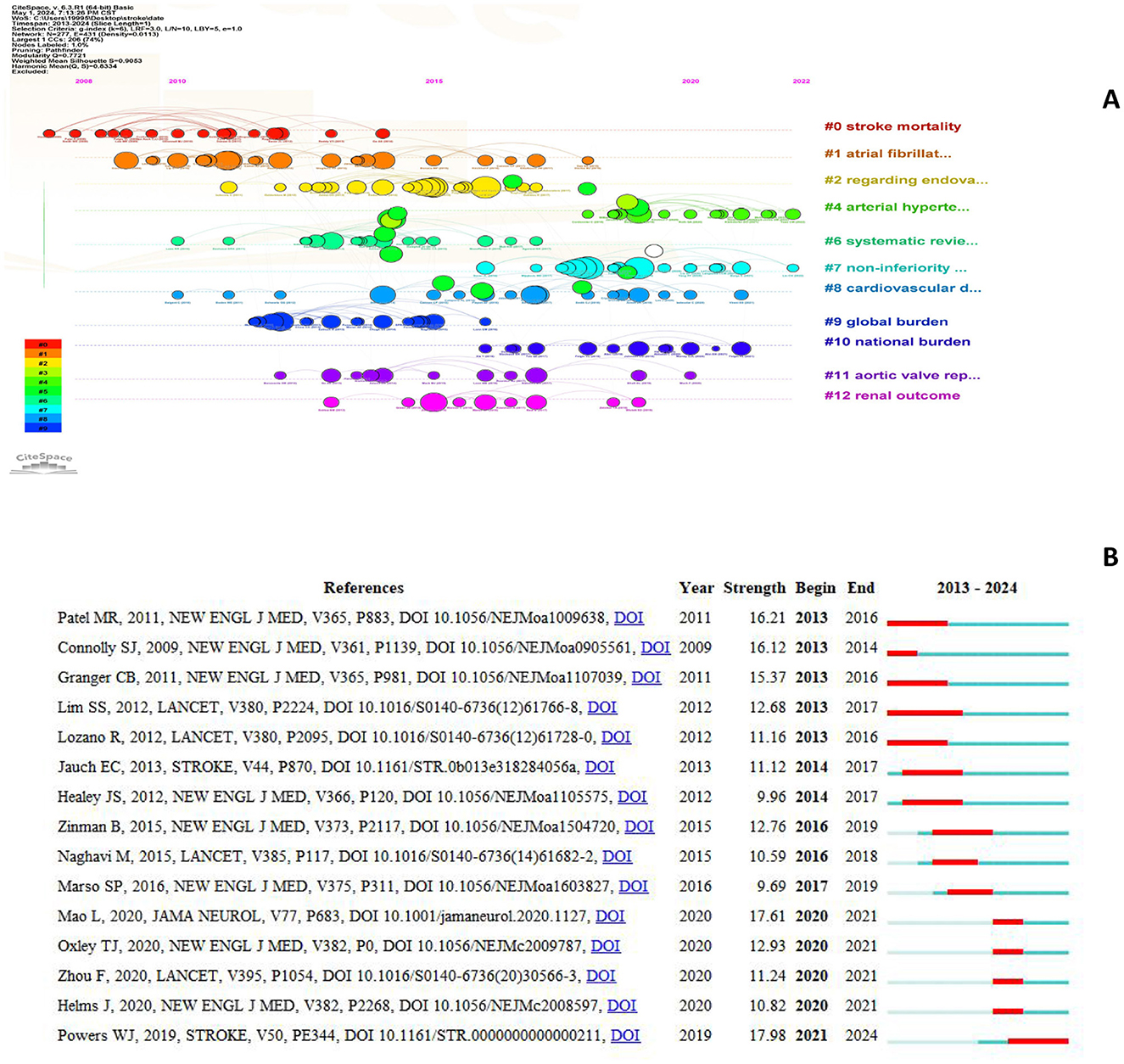
3.7 Analysis of citation bursts
The top 15 most-cited references are shown in Figure 9.
A burst occurs when a publication receives a significantly higher
number of citations than usual and lasts for at least 2 years (Jiang et al., 2022).
The blue line represents the observation period from 2013 to 2024 and
the red line indicates the burst time. The article “Guidelines for the
early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to
the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a
guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart
Association/American Stroke Association,” published in the stroke, has
the highest citation burst value (citation burst = 17.98) between 2013
and 2024. This is the latest citation outbreak in 2021 and has continued
to date (Powers et al., 2019).
The guidelines detail prehospital care, emergency evaluation,
intravenous and intravenous treatment, and in-hospital management,
including appropriately instituted secondary prevention measures within
the first 2 weeks. The guidelines support the overall concept of a
stroke care system and provide recommendations based on available
evidence to guide physicians in the care of patients with acute arterial
ischemic stroke. Additionally, the 2012 Lancet article “A comparative
risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk
factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic
analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010” cited the longest
outbreak duration (=5 years). This study suggests that in 2010, the
three leading risk factors for the global disease burden were high blood
pressure, tobacco smoking, and household air pollution from solid fuels
(Lim et al., 2012).
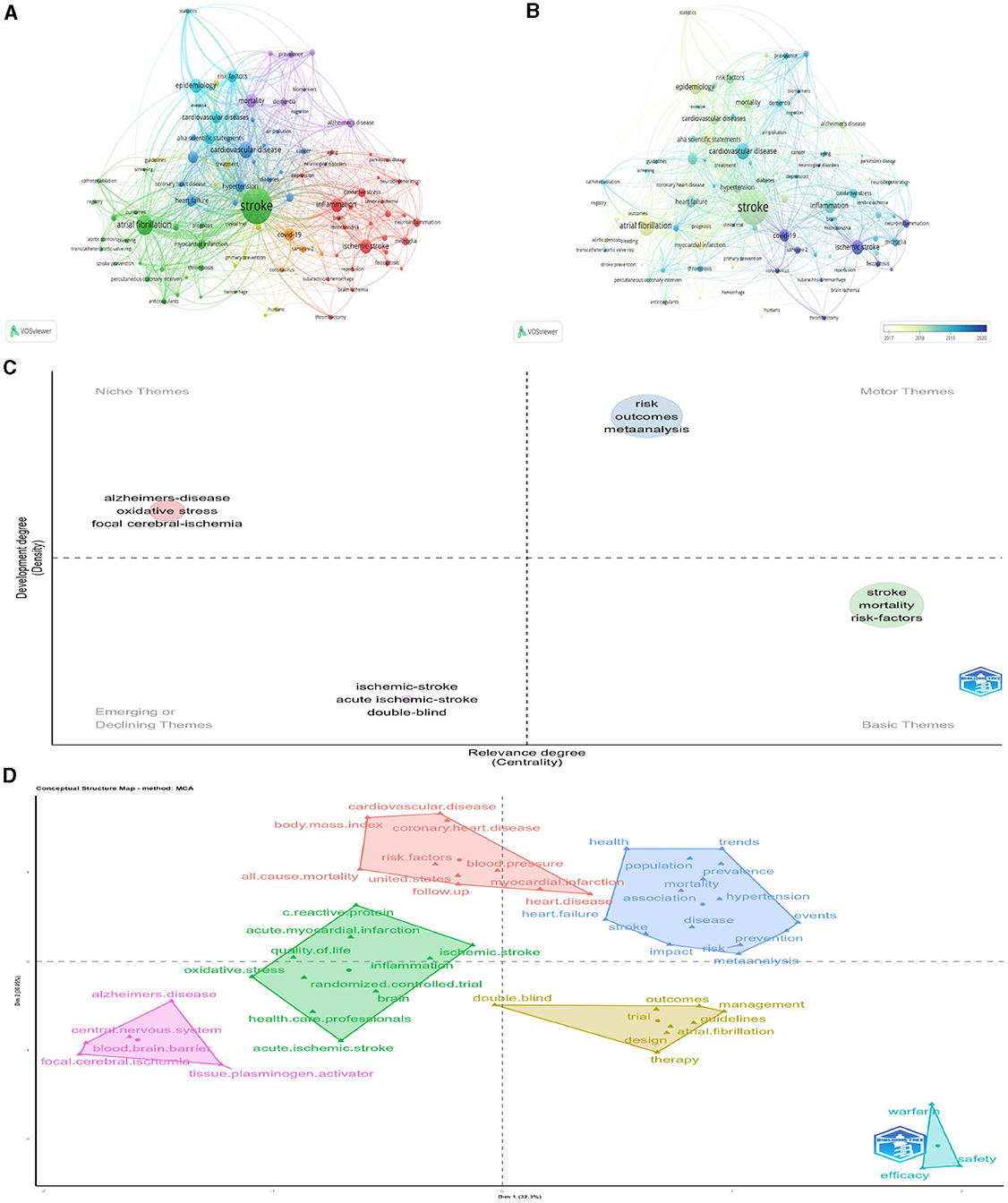
3.8 Frequency and clustering analysis of keywords
Of the 3,625 keywords, 99 occurred at least 10 times and
were analyzed further. If keywords had similar connotations, they were
consolidated. Figure 10A
illustrates the network visualization of these keywords, where the size
of the nodes represents the keyword frequency and the proximity of the
nodes signifies the strength of the relationships (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017). Figure 10A
presents a network visualization of these keywords. Group 1, depicted
in green, concentrated on cardiocerebrovascular diseases linked to
stroke, including atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, and
“thrombosis.” Group 2, shown in blue, emphasized high-risk factors
associated with cardiovascular diseases and meta-analyses, using
keywords such as “cardiovascular disease,” “hypertension,” “obesity,”
“diabetes,” and “meta-analysis.” The third light blue cluster primarily
focused on epidemic risk factors associated with cardiovascular
diseases, involving “cardiovascular disease,” “epidemiology,” “risk
factors,” and “statistics.” Group 4 included the incidence, prevalence,
and mortality rate of stroke-related diseases. Group 5, represented in
red, centered on the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke with keywords such
as “ischemic stroke,” “inflammation,” “oxidative stress,” and
“neuroinflammation.” Figure 10B shows a visualization of the temporal overlapping of keywords.
To reflect critical themes in stroke research, a topic map and topic classification of keywords were created (Figures 10C, D).
The keywords “risk,” “outcome,” “meta analysis” are motor themes, have
high density and high centrality, which are important and developing
well at present. The keywords “stroke,” “mortality,” “risk-factors”
belong to basic theme, have high centrality but less dense, which
represent important but not well-developed in the research field. The
keywords including “Alzheimer's disease,” “oxidative stress,” and “focal
cerebral ischemia” belong to niche theme, have high density and low
centrality, which means that they are well-developed but not important
to the current field. The keywords “ischemic-stroke,” “acute
ischemic-stroke,” and “double-blind” belong to emerging theme, have high
centrality and low density. Combined with overlay visualization, this
research field is relatively marginal; however, there has been a trend
of emergence and development in recent years.
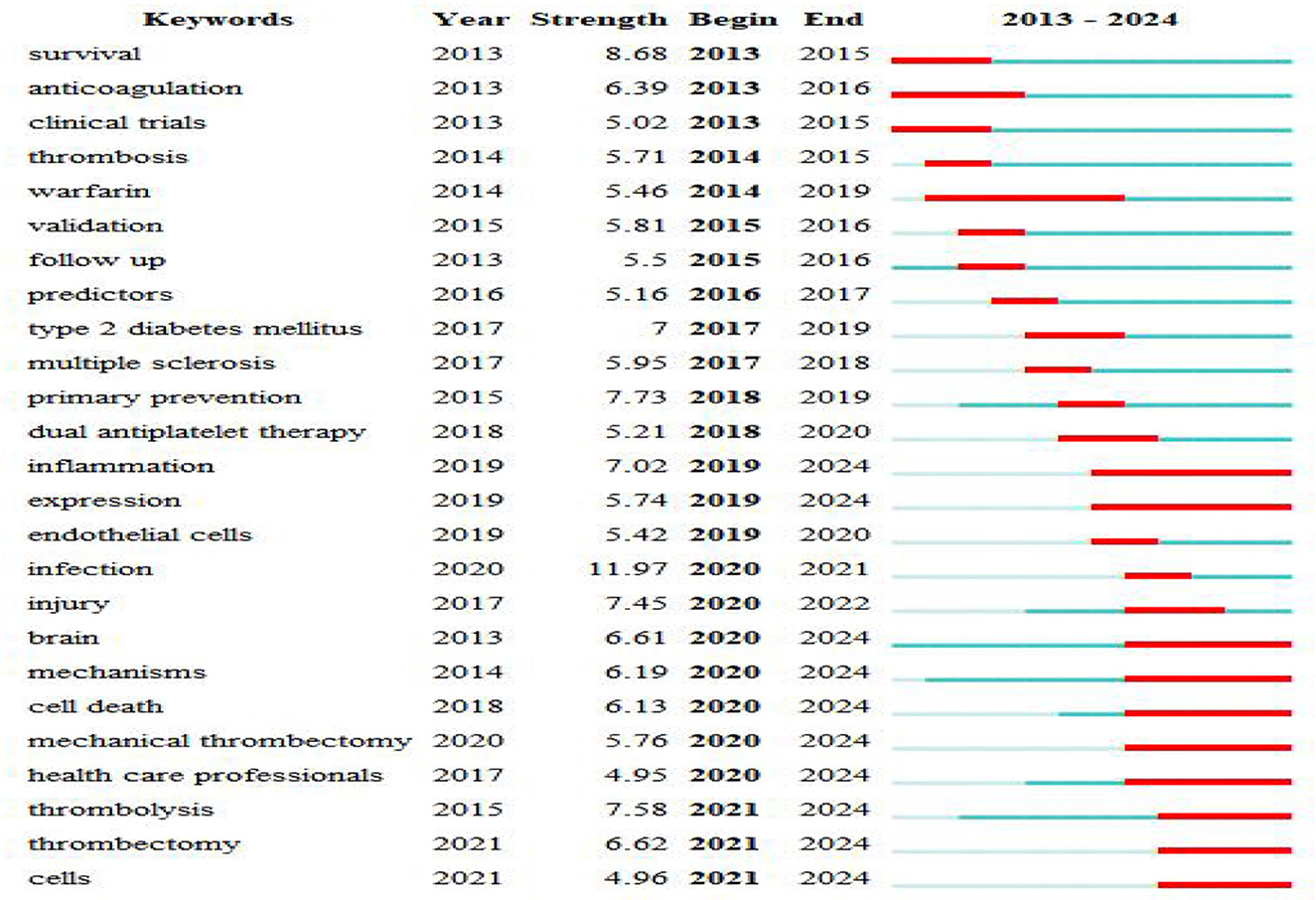
3.9 Analysis of keywords bursts
Figure 11
shows the 25 keywords with the highest citation bursts lasting for more
than a year. The keywords “warfarin” (2014–2019), “inflammation”
(2019–2024), and “expression” (2019–2024) have received the most
consistent focus. Beyond “inflammation” “expression”, other keywords
such as “brain” (2020–2024), “mechanisms” (2020–2024), “cell death”
(2020–2024), “mechanical thrombectomy” (2020–2024), “health care
professionals” (2020–2024), “thrombolysis” (2021–2024), “thrombectomy”
(2021–2024), and “cells” (2020–2024) have also emerged recently. These
findings suggest that future studies should focus on these areas.
4 Discussion
This study conducted a bibliometric review of 2,509
highly cited studies on stroke. The data indicate a consistent growth
trend in the frequency of publications and the mean citation count for
these pivotal works. From 2013 to 2023, the mean number of publications
per annum among these influential articles was 227.73, with a
corresponding annual citation average of 56.28. The gravity of stroke,
as measured by its incidence, prevalence, case-fatality rate, and
disability-adjusted life-years, underscores the enduring focus on stroke
research by medical practitioners and public health professionals.
Robust annual output within this scientific domain reflects this
priority.
The top 10 nations, accounting for 82.66% of the
referenced studies, are led by the United States, which contributes to a
third (36.11%) of the total publications. The US also stands out for
its international collaboration, leading seven of the top 10 slots in
terms of collaborative frequency. These statistics underscore the US's
preeminent role in global stroke research, a status likely attributable
to its robust economic climate, significant investment in medical
research, and prioritization of stroke studies. This field is poised to
advance further through increased international scholarly collaboration,
that is expected to enhance global research.
The top 10 academic institutions are largely distributed
in the US, reflecting the country's prominent role in research output.
While China leads in terms of the quantity of publications, none of its
institutions are in the top 10. The UK holds the third position in terms
of publications, with the University of Oxford coming in third with 116
papers in the top 10. Canada followed closely in fifth place, and the
University of Toronto ranked fifth with 103 papers. Many collaborative
studies have suggested that international partnerships are the key to
enhancing research performance, particularly in resource-constrained
environments.
Academic publishing relies heavily on peer-reviewed
journals, which often conduct significant research within the field.
Researchers can use the frequency of journal publications in the field
of stroke to identify potential journals to submit their work. The New
England Journal of Medicine tops the list with 223 publications, whereas
Lancent has the highest impact factor (IF = 168.90), followed by the
Journal of New England Journal of Medicine (IF = 158.50). Impact factor
and journal citation reports (JCR) are standard metrics for assessing
journal influence. JCR categorizes journals into quartiles (Q1–Q4) based
on their IF, and all the top 10 journals by the number of papers are in
the Q1 category. Furthermore, the top 10 journals are all based in the
US and the UK, with the US accounting for 70% and the UK accounting for
30%.
The objective of this study was to address the topic of
research extensively investigated by scholars over a defined period. The
number of citations is considered a metric of a publication's academic
impact (Xu and Sun, 2020).
Publications with a high number of citations tend to encapsulate the
core issues within a given research domain. Identifying these hotspots
involves analyzing citation frequencies and pinpointing works that are
frequently referenced. In this instance, nine articles qualified as
highly cited (over 4,000 citations) and strongly linked (over 10
connections). These top-tier articles were published between 2015 and
2019 and predominantly appeared in the New England Journal of Medicine
(four), Circulation (three), Lancet (one), and Stroke (one).
Three articles published in Circulation (Benjamin et al., 2017, 2018, 2019),
penned by the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and
Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee,
collated the latest Figures on heart disease, stroke, and cardiovascular
risk factors used in the AHA My Life Check. These articles were updated
in 2017, 2018, and 2019 and were entitled “Heart Disease and Stroke
Statistics.” The 2017 update emphasized the advantages of substantial
blood pressure (BP) reduction in clinical trials (Benjamin et al., 2017),
which reduced the risk of stroke outcomes. It also highlighted that
adherence to a Mediterranean diet abundant in nuts and olive oil was
associated with a lower risk of stroke. The 2018 update pointed out that
there were significant racial and regional disparities in stroke risks
and outcomes, with the impact of hypertension management on stroke risk
being more significant in those receiving intense treatment (Benjamin et al., 2018).
The 2019 update found that although age-standardized mortality rates
for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke worldwide decreased from 1990 to
2015, the actual number of annual stroke cases, related deaths, and
disability-adjusted life years increased. The majority of the global
stroke burden falls in low- and middle-income countries (Benjamin et al., 2019).
Four key studies were published in the New England Journal of Medicine, in 2015. Goyal et al. (2015)
suggested that urgent endovascular treatment could improve functional
recovery and reduce death rates in patients with acute ischemic stroke
caused by a blocked main artery, limited brain damage, or sufficient
blood flow through alternative routes. Campbell et al. (2015)
demonstrated the advantages of early blood clot retrieval using the
Solitaire FR stent retriever system, as opposed to using the
clot-dissolving drug alteplase alone, in patients with ischemic stroke
and signs of salvageable brain tissue on CT perfusion scans.
Furthermore, Berkhemer et al. (2015)
and his associates confirmed the effectiveness and safety of
intra-arterial treatment within the first 6 h after stroke in patients
with blockage of the main brain artery in the frontal circulation.
Lastly, Sarafidis and Tsapas (Sarafidis and Tsapas, 2016)
reported that patients with type 2 diabetes and were at high risk of
cardiovascular issues who were treated with empagliflozin experienced a
lower incidence of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality when
the medication was included in their standard care.
The 2016 findings from Goyal et al. (2016),
published in The Lancet, indicated that endovascular thrombectomy can
be advantageous for the majority of patients experiencing acute ischemic
stroke due to blockage in the anterior circulation, regardless of
individual patient traits or regional location. This has contributed to a
shift in the treatment paradigm for acute ischemic stroke, which is
caused by clot-blocking of blood vessels in the brain. Endovascular
thrombectomy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves removal of
the clot from the affected blood vessel using a catheter threaded
through the arteries to the site of blockage.
In 2018, Powers et al. from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (Powers et al., 2019)
Published A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals, Guidelines for the
Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke, which are based
on the best evidence currently available, guidelines detailing
prehospital care, urgent and emergency evaluation and treatment with
intravenous and intra-arterial therapies, and in-hospital management,
including secondary prevention measures that are appropriately
instituted within the first 2 weeks. These guidelines support the
overarching concept of stroke care systems in both pre-hospital and
hospital settings.
Because keywords affect the core content of a study,
co-occurrence analysis can identify high frequency keywords that appear
in different studies, thus helping researchers to quickly grasp research
hotspots. The most frequently used keywords were “risk,” “stroke,” and
“mortality.” The mean “stroke” frequency was 255. From the topic map and
subject word classification results, we know that mortality and risk
factors of stroke, as basic themes, are an important part of the
research field; however, further research is required. Meta-analysis of
stroke risk and outcome is a motor theme, has been performed extensively
in this field and is relatively mature, and some related studies have
been conducted on “Alzheimer's disease,” “oxidative stress,” and “focal
cerebral ischemia,” but the subject area is less central, so the
development in the subject field is currently less important. “Ischemic
stroke,” “acute Ischemic stroke,” and “double-blind experiment” belong
to emerging themes, because ischemic stroke has the highest incidence of
all stroke types, and is expected to be one of the important research
topics in this field in the future.
In the factor analysis, the top 50 keywords were divided
into six major categories, with four major categories related to the
center. The first classified topics are: fatal related factors,
meta-analysis, mortality mechanism, epidemic trend of event occurrence,
prevention strategies and other related topics. The second major
category includes: risk factors for stroke and various causes of death,
including cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and body mass index. The
third category of topics was mainly divided into: ischemic stroke and
acute ischemic stroke inflammation, acute myocardial infarction,
randomized controlled trials, health care, and quality of life. These
keywords are classified re?ect the core content of the stroke study.
The CiteSpace “burst detection” method identifies keywords or cited references with significant changes over time (Chen, 2006).
Researchers can use keywords and cited references with burst features
to explore hotspots. In this study, “inflammation,” “expression,”
“mechanisms, “thrombolysis,” “thrombectomy,” and “cell” etc. were
keywords that continued to burst as of 2024. This suggests that the
pathogenesis of stroke, thrombolysis, and thrombectomy is a future
research hotspot. In addition, one cited reference will continue to
burst by 2024. The guidelines in this literature provide general
recommendations based on currently available evidence to guide
clinicians caring for adult patients with acute arterial ischemic
stroke.
5 Conclusions
This article conducted a bibliometric analysis of 2,509
highly cited stroke research papers, revealing the current status and
development trends in this field. The following is an in-depth
exploration of the analysis results:
5.1 Research hotspots and future directions
Inflammation and thrombolytic therapy: the persistent
burst of keywords such as “inflammation” and “thrombolysis” indicates
that the pathogenesis of stroke, thrombolytic therapy, and thrombectomy
will be the focus of future research. This suggests the need to further
investigate the role of inflammation in the onset and development of
stroke and develop more effective thrombolytic therapy strategies.
Mechanism research: the burst of keywords such as “mechanism” and “cell”
indicates that stroke researchers are increasingly focusing on studying
the pathogenesis. This study provides a theoretical basis for the
development of new therapeutic drugs and preventive strategies.
Neuroimaging: the emergence of keywords such as “imaging” and “CT scan”
suggests that neuroimaging techniques are becoming increasingly widely
used in the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of stroke. In the
future, it will be necessary to further develop and apply new imaging
techniques to assess the pathophysiological changes and treatment
effects of stroke more accurately. Personalized treatment: the emergence
of keywords such as “gene” and “epigenetics” indicates that
personalized treatment will become an important direction in stroke
treatment. Further research is needed to investigate the role of genes
and epigenetics in the pathogenesis of stroke to develop more precise
treatment plans.
5.2 National and regional cooperation
The leading position of the United States in the field of
stroke research is undeniable, with research output and influence
ranking first globally. China ranks second in terms of research output;
however, its research influence still needs to be improved, and
international cooperation is an important way to improve the level of
stroke research. There is extensive cooperation between developed
countries, such as the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, and
Canada. In the future, it will be necessary to strengthen cooperation
with other countries, especially developing countries, to jointly
promote stroke research.
5.3 Research institutions and journals
Institutions such as Harvard Medical School and Brigham
and Women's Hospital have made outstanding contributions to the field of
stroke research, and their research results are of great significance
in promoting the development of this field. Top journals such as the New
England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet have published a large
number of high-quality stroke research papers, playing an important role
in promoting the development of this field.
5.4 Researcher influence
Researchers such as Yusuf S have made significant
contributions to the field of stroke research, and their research
results are of great significance in promoting the development of this
field. In the future, more excellent stroke researchers need to be
trained to promote the development of this field.
Stroke research is a field full of challenges and
opportunities. In the future, we need to strengthen international
cooperation, focus on research hotspots, and train outstanding stroke
researchers to promote the development of this field and to make greater
contributions to human health.
6 Strengths and limitation
This study had some limitations. First, it exclusively
incorporates extensively highly cited English-language articles indexed
in the WoSCC repository. Although WoSCC encapsulates the most premium
research, it can potentially skew our findings. Second, the inclusion of
recently released premium research may be compromised by a time lag in
citations, necessitating future updates. Nonetheless, this study
provides substantial aid to researchers in the field by offering
insights into the progression, focal points, trends, and cutting-edge
developments in stroke research as well as highlighting areas calling
for additional investigation.
Author contributions
LF: Formal analysis, Resources, Software, Visualization,
Writing – original draft. FS: Formal analysis, Supervision, Validation,
Writing – review & editing. SW: Funding acquisition, Supervision,
Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in
the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be
construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of
the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated
organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers.
Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be
made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the
publisher.
 Li Fan
Li Fan Fuyan Shi1
Fuyan Shi1 Suzhen Wang
Suzhen Wang