This article has this line in it:
Targeting dangerous inflammation inside artery plaque
A research team showed that a nanotherapeutic medicine can halt the growth of artery plaque cells resulting in the fast reduction of the inflammation that may cause a heart attack.
Which means our stroke researchers should be all over this to figure out a way to remove all the plaque in brain arteries preventing your next stroke.
Multifunctional nanomedicine strategies to manage brain diseases
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2022)
Abstract
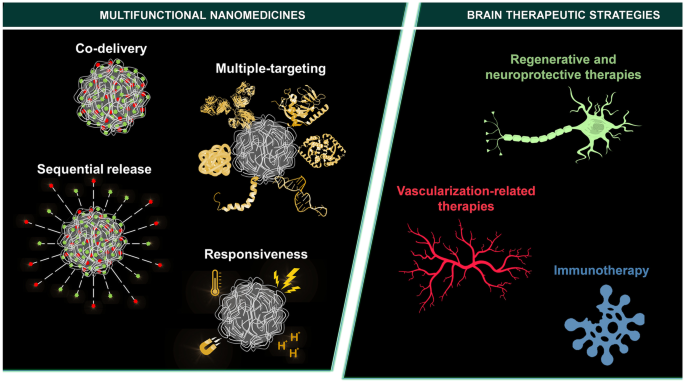
Brain diseases represent a substantial social and economic burden, currently affecting one in six individuals worldwide. Brain research has been focus of great attention in order to unravel the pathogenesis and complexity of brain diseases at the cellular, molecular, and microenvironmental levels. Due to the intrinsic nature of the brain, the presence of the highly restrictive blood–brain barrier (BBB), and the pathophysiology of most diseases, therapies can hardly be considered successful purely by the administration of one drug to a patient. Apart from improving pharmacokinetic parameters, tailoring biodistribution, and reducing the number of side effects, nanomedicines are able to actively co-target the therapeutics to the brain parenchyma and brain lesions, as well as to achieve the delivery of multiple cargos with therapeutic, diagnostic, and theranostic properties. Among other multivalent effects that can be personalized according to the disease needs, this represents a promising class of novel nanosystems, termed multifunctional nanomedicines. Herein, we review the principal mechanisms of therapeutic resistance of the most prevalent brain diseases, how to overcome this therapeutic resistance through the use of multifunctional nanomedicines that tackle multiple fronts of the disease microenvironment, and the promising therapeutic responses achieved by some of the most cutting-edge multifunctional nanomedicines reported in literature.
Graphical Abstract
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution.
No comments:
Post a Comment