I haven't seen research that claims 100% recovery using VR. So, let's do things in the correct order.
- Get VR to 100% recovery
- Switch to glove free while maintaining 100% recovery!
New glove free VR tech could transform rehab
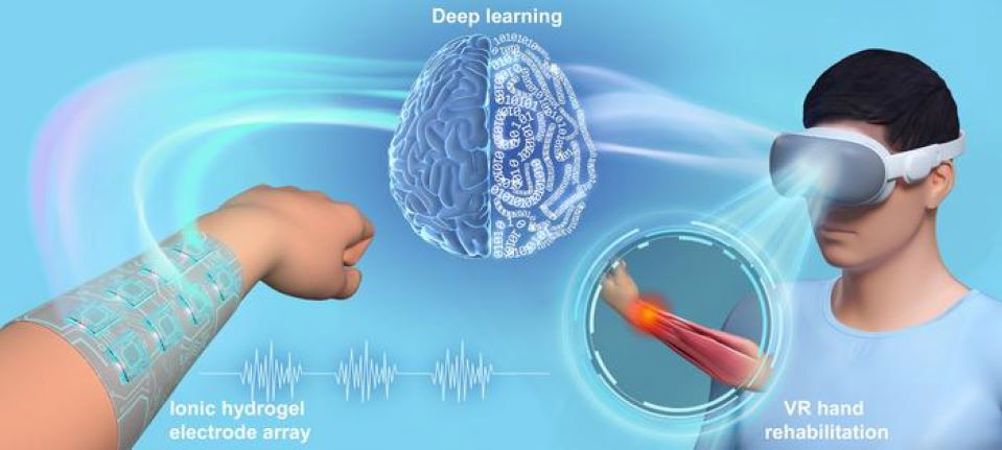
Researchers in China have created a deep learning-based, non-hand-worn VR rehabilitation system using ionic hydrogel electrodes to improve(NOT GOOD ENOUGH! 100% recovery is expected by survivors!) therapy for stroke and osteoarthritis patients.

Developed by a team at Zhengzhou University, the system integrates deep learning with ionic hydrogel electrodes to recognise hand gestures based on electromyographic (EMG) signals.
Conventional hand rehabilitation therapy often relies on bulky mechanical gloves that can increase the strain on a patient’s hand. These devices are also complex to operate and often require specialised medical facilities.
The newly developed system eliminates the need for heavy, hand-worn equipment, offering a load-free and flexible rehabilitation solution. Patients can engage in rehabilitation exercises anywhere and anytime, without having to wear such cumbersome devices.
The system’s ionic hydrogel electrodes are wet-adhesive, self-healing, and conductive. These electrodes, applied directly to the forearm, collect EMG signals generated by hand movements. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) then process these signals to recognise a range of hand gestures.
In a trial, the system is said to have achieved 97.9 per cent accuracy in recognising 14 different Jebsen hand rehabilitation gestures, a standardised and objective measure of fine and gross motor hand functions that uses simulated activities of daily living.
This recognition is linked to a Virtual Reality (VR) platform where patients can interact with virtual environments.
In a statement, lead researcher Professor Yanchao Mao said: “Our goal is to eliminate the need for cumbersome, mechanical rehabilitation gloves. By integrating deep learning and ionic hydrogel technology, we can provide patients with a more comfortable, accessible, and efficient rehabilitation process. Patients can now perform immersive VR rehabilitation exercises in their homes, without the limitations of specialised equipment or facilities.”
According to the team, the system could ‘dramatically improve’ the quality of life for patients undergoing hand rehabilitation, particularly those with mobility challenges. Moreover, this deep learning-assisted VR rehabilitation system can potentially be adapted to other areas of physical therapy.
The team plans to further refine the system’s gesture recognition accuracy and expand its capabilities in fields such as stroke recovery, musculoskeletal injuries, and geriatric rehabilitation.
The team’s research is detailed in Nano Research
No comments:
Post a Comment