What does your doctor have to say about this?
Can coenzyme Q10 reduce the risk of side effects from statins?
The latest here:
Coenzyme Q10 attenuates age-associated neurodegeneration via modulation of autophagy and neuroinflammation in aged rats
Abstract
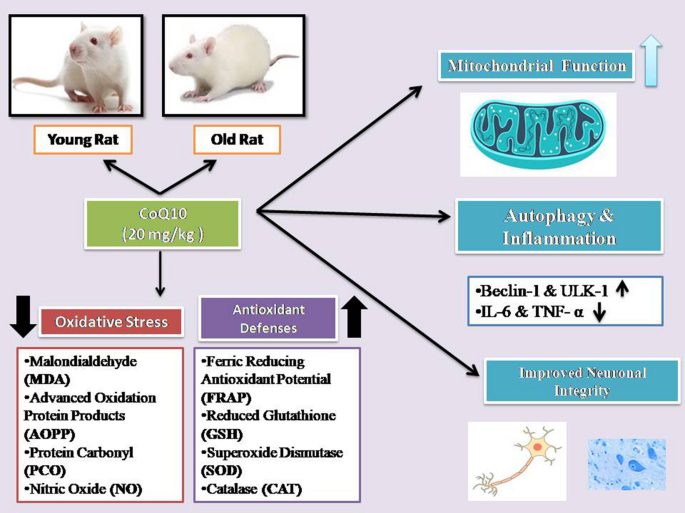
This study investigates the neuroprotective potential of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in aging rats, with emphasis on its roles in modulating autophagy and reducing inflammaging. Male Wistar rats, both young (4 months) and aged (24 months), were orally administered CoQ10 at a dose of 20 mg/kg body weight for 28 days. Biochemical analysis revealed a significant enhancement in antioxidant defenses, as evidenced by elevated ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), reduced glutathione (GSH), and increased activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT). In parallel, levels of oxidative stress biomarkers—including malondialdehyde (MDA), advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP), protein carbonyls (PCO), and nitric oxide (NO)—were significantly reduced. CoQ10 supplementation also restored mitochondrial function, as indicated by increased activities of electron transport chain complexes in the brain. Gene expression analysis via reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) showed up-regulation of autophagy markers Beclin-1 and ULK-1, alongside down-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α, suggesting a reduction in neuroinflammation. Histopathological analysis supported these findings, demonstrating improved structural integrity of brain cells in CoQ10-treated rats. Overall, these results indicate that CoQ10 exerts multifaceted neuroprotective effects through enhancement of antioxidant defenses, restoration of mitochondrial function, activation of autophagy, and suppression of inflammation, thereby offering a promising intervention to mitigate age-associated neurodegeneration.
Graphical Abstract
No comments:
Post a Comment